What’s Inside your Hearing Aid?
May 02, 2022
Today’s hearing aids had come a long, long way since its invention in the 17th century. Modern hearing aids come with sophisticated technology that makes it nothing short of a scientific marvel. And, not to forget, it helps millions of people hear and enjoy life better.
If you’re a hearing aid user or contemplating using one, it’s a great idea to understand the basics of what’s inside it and how it works. It not only helps you appreciate these marvelous technological inventions but also enables you to troubleshoot it if any errors occur.
Hearing aids are of two major types:
- RITE (Receiver-in-the-ear) hearing aid
- FITE (Fully-in-the-ear) hearing aid
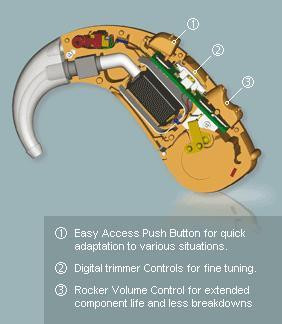
Regardless of the hearing aid you use, it contains the following three major components.
- The Microphone
The functioning of the hearing aid starts with the microphone. It picks up the various sounds from the environment and converts it into electric signals that are fed to the processor.
When you buy hearing aids, look for advanced models that can differentiate between different sounds helping to separate background noise from speech. These models segregate sounds into various categories, processing them differently, thereby providing the wearer with a better hearing experience.
Microphones can be further classified into two types:
- Directional microphones – As the name implies, this picks up sounds predominately from one direction, i.e., sounds coming in from the front of the wearer. Directional microphones are great when the user wants to recognize and understand speech in a noisy place. To give an example, the Siemens Signia Pure Primax model makes use of directional microphones. Make sure to check out the latest Siemens hearing aid prices before you choose the right model that works for you.
- Omni-directional microphones – From the name, you would have guessed it. These microphones pick up sounds from all directions. It helps the user orient them better in a noisy environment.
Nearly all modern hearing aids have both these types of microphones to provide users with a more natural listening experience. Siemens
- The Processor
It’s also known as the amplifier. It’s the small chip that acts as the brain of the hearing aid. It converts the electric signals picked up by the microphone into digital signals. The microprocessor decides how the digital signal has to be amplified based on the wearer’s needs. The severity of the user’s hearing loss determines the amplification levels.
To give an example, if the person has low to moderate hearing loss, then the signals are amplified only a little. The power of amplification depends on the hearing capabilities of the wearer. This is why swapping or exchanging hearing aids with another wearer is not recommended.
The processor also cuts down other distracting sounds in the environment like wind, background noises, etc. Once the processor has optimized the sounds picked, it converts the signal – from digital to analog, which goes to the next component.
- The Receiver
Also known as the speaker, this is the final component of the hearing aid. The primary role of a hearing aid is to deliver sounds from the environment directly to your ear. And, the receiver does that. It transforms the electric signals from the processor into sound waves that are passed into the wearer’s inner ear.
The position of the receiver depends on the severity of the hearing loss and lifestyle preferences. In some hearing aids, the speaker is placed directly into the ear canal. While in other models – the receiver is connected to a small tube inserted into the ear.
Apart from these three major components, hearing aids have other minor but equally important parts like:
- Battery – This is the power source for all the parts of the hearing aid.
- Volume Control – This helps the wearer to increase or decrease the intensity of the sound. It may not be present in all styles.
- Wax guard – This prevents ear wax from clogging the critical components of the hearing aid.
Understanding the components of your hearing aid will help you make informed choices while comparing different hearing aids for sale. Make sure to learn the features of your hearing aid, to pick the right one that suits your medical requirements as well as your lifestyle preferences.